cat 명령어와 grep 명령어를 통해 특정년도의 수상자를 검색
입력
cat soccer_scores.csv | grep "1959"출력
1959,Dunav,2
cat, grep or 명령, wc 명령을 통한 갯수 출력
입력
cat two_cities.txt | grep -e "Sydney Carton" -e "Charles Darnay" | wc -l출력
77
Bash script anatomy
기본적으로 /usr/bash if you installed bash in basic directory, bash usually located in /usr/bash
#!/usr/bash어원 유닉스 계열에서는 sharp(#) + bang(!) 합성어로 sha-bang 이라 함
확장자 명 file extension .sh
bash 실행 위치 /bin/bash의 경우
#!/bin/bash
cat server_log_with_todays_date.txtsoccer_scores.csv에서 , 구분자로 2번째에 있는 팀명 가져오기
uniq 중복제거
cat soccer_scores.csv | cut -d "," -f 2 | tail -n +2 | sort | uniq -c
soccer_scores.csv sed 명령으로 문자열 치환 후 soccer_scores_edited.csv에 저장
cat soccer_scores.csv | sed 's/Cherno/Cherno City/g' | \
sed 's/Arda/Arda United/g' > soccer_scores_edited.csv
Stdin-Stdout graphically
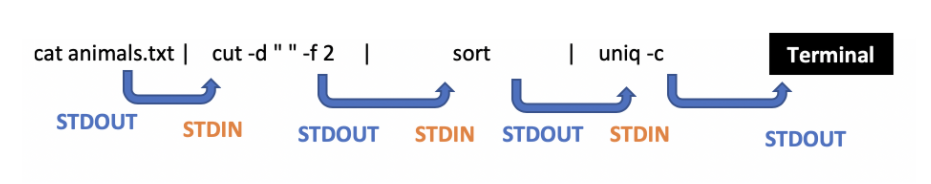
stdin argv 차이

@ entire argv array
# argv size
# Echo the first and second ARGV arguments
echo $1
echo $2
# Echo out the entire ARGV array
echo $@
# Echo out the size of ARGV
echo $#입력
bash script.sh Bird Fish Rabbit출력
Bird
Fish
Bird Fish Rabbit
3
bash 작성 script.sh
# Echo the first ARGV argument
echo $1
# Cat all the files
# Then pipe to grep using the first ARGV argument
# Then write out to a named csv using the first ARGV argument
cat hire_data/* | grep "$1" > "$1".csvshell 에서 Seoul 과 Tallinn 각 csv 파일 생성
repl:~/workspace$ bash script.sh Seoul
Seoul
repl:~/workspace$ bash script.sh Seoul Tallinn
Seoul
repl:~/workspace$ bash script.sh Tallinn
Tallinn
bash에서 변수생성시 스페이스바는 적용 x

따옴표에 따른 차이
' 은 문자열 그대로를 보냄
" 은 변수를 보낼 수 있음

data 는 원래 명령 옵션으로 날짜를 출력하는데 이를 bacticks를 통해 표현 가능
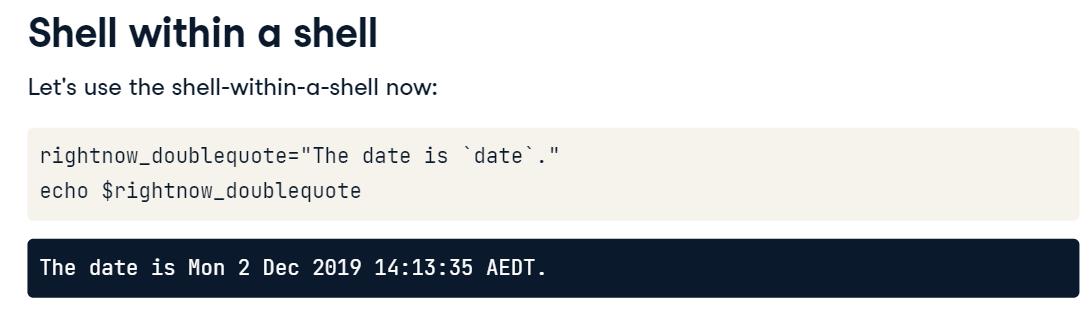
괄호 : 호출할 수 있는 다른 방법

bash 실행
# Create the required variable
yourname="Sam"
# Print out the assigned name (Help fix this error!)
echo "Hi there $yourname, welcome to the website!"
숫자 계산

scale을 통한 자리수 설정도 가능

bash에서 double bracket으로 표현해 숫자로 인식하는 방식

bc를 이용한 방식

# Get first ARGV into variable
temp_f=$1
# Subtract 32
temp_f2=$(echo "scale=2; $temp_f - 32" | bc)
# Multiply by 5/9 and print
temp_c=$(echo "scale=2; $temp_f2 * 5 / 9" | bc)
# Print the celsius temp
echo $temp_c
# Create three variables from the temp data files' contents
temp_a=$(cat temps/region_A)
temp_b=$(cat temps/region_B)
temp_c=$(cat temps/region_C)
# Print out the three variables
echo "The three temperatures were $temp_a, $temp_b, and $temp_c"
bash 에서 array 생성


배열 추가
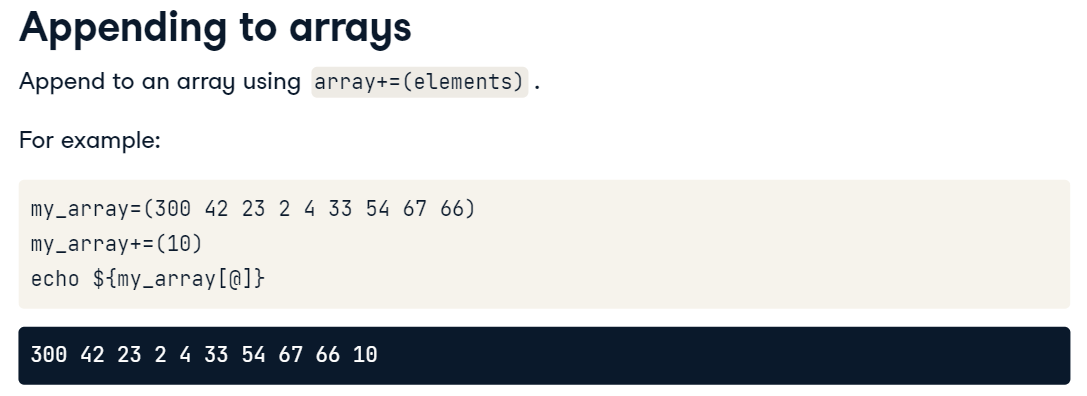
associative array - 선언 추가

생성

배열 추가
# Create a normal array with the mentioned elements using the declare method
declare -a capital_cities
# Add (append) the elements
capital_cities+=("Sydney")
capital_cities+=("Albany")
capital_cities+=("Paris")전체 출력, 길이 출력
# The array has been created for you
capital_cities=("Sydney" "Albany" "Paris")
# Print out the entire array
echo ${capital_cities[@]}
# Print out the array length
echo ${#capital_cities[@]}
associative array
# Create empty associative array
declare -A model_metrics
# Add the key-value pairs
model_metrics[model_accuracy]=98
model_metrics[model_name]="knn"
model_metrics[model_f1]=0.82선언하면서 변수 입력
# Declare associative array with key-value pairs on one line
declare -A model_metrics=([model_accuracy]=98 [model_name]="knn" [model_f1]=0.82)
# Print out the entire array
echo ${model_metrics[@]}
key 출력
# An associative array has been created for you
declare -A model_metrics=([model_accuracy]=98 [model_name]="knn" [model_f1]=0.82)
# Print out just the keys
echo ${!model_metrics[@]}문제
# Create variables from the temperature data files
temp_b="$(cat temps/region_B)"
temp_c="$(cat temps/region_C)"
# Create an array with these variables as elements
region_temps=($temp_b $temp_c)
# Call an external program to get average temperature
average_temp=$(echo "scale=2; (${region_temps[0]} + ${region_temps[1]}) / 2" | bc)
# Append average temp to the array
region_temps+=($average_temp)
# Print out the whole array
echo ${region_temps[@]}
if 문



multiple condition

같은 결과


# Extract Accuracy from first ARGV element
accuracy=$(grep Accuracy $1 | sed 's/.* //')
# Conditionally move into good_models folder
if [ $accuracy -ge 90 ]; then
mv $1 good_models/
fi
# Conditionally move into bad_models folder
if [ $accuracy -lt 90 ]; then
mv $1 bad_models/
fi
# Create variable from first ARGV element
sfile=$1
# Create an IF statement on sfile's contents
if grep -q 'SRVM_' $sfile && grep -q 'vpt' $sfile ; then
# Move file if matched
mv $sfile good_logs/
fi
for문

global expansions *

while 문

# Use a FOR loop on files in directory
for file in inherited_folder/*.R
do
# Echo out each file
echo $file
done
# Create a FOR statement on files in directory
for file in robs_files/*.py
do
# Create IF statement using grep
if grep -q 'RandomForestClassifier' $file ; then
# Move wanted files to to_keep/ folder
mv $file to_keep/
fi
done
case 문

# Create a CASE statement matching the first ARGV element
case $1 in
# Match on all weekdays
Monday|Tuesday|Wednesday|Thursday|Friday)
echo "It is a Weekday!";;
# Match on all weekend days
Saturday|Sunday)
echo "It is a Weekend!";;
# Create a default
DEFAULT)
echo "Not a day!";;
esac
# Use a FOR loop for each file in 'model_out'
for file in model_out/*
do
# Create a CASE statement for each file's contents
case $(cat $file) in
# Match on tree and non-tree models
*"Random Forest"*|*GBM*|*XGBoost*)
mv $file tree_models/ ;;
*KNN*|*Logistic*)
rm $file ;;
# Create a default
*)
echo "Unknown model in $file" ;;
esac
done
bash 함수

static 변수

# Create function
function upload_to_cloud () {
# Loop through files with glob expansion
for file in output_dir/*results*
do
# Echo that they are being uploaded
echo "Uploading $file to cloud"
done
}
# Call the function
upload_to_cloud# Create function
function what_day_is_it {
# Parse the results of date
current_day=$(date | cut -d " " -f1)
# Echo the result
echo $current_day
}
# Call the function
what_day_is_it
함수 리턴값 저장

# Create a function
function return_percentage () {
# Calculate the percentage using bc
percent=$(echo "scale=2; 100 * $1 / $2" | bc)
# Return the calculated percentage
echo $percent
}
# Call the function with 456 and 632 and echo the result
return_test=$(return_percentage 456 632)
echo "456 out of 632 as a percent is $return_test%"
# Create a function
function get_number_wins () {
# Filter aggregate results by argument
win_stats=$(cat soccer_scores.csv | cut -d "," -f2 | egrep -v 'Winner'| sort | uniq -c | egrep "$1")
}
# Call the function with specified argument
get_number_wins "Etar"
# Print out the global variable
echo "The aggregated stats are: $win_stats"# Create a function with a local base variable
function sum_array () {
local sum=0
# Loop through, adding to base variable
for number in "${test_array[@]}"
do
sum=$(echo "$sum + $number" | bc)
done
# Echo back the result
echo $sum
}
# Call function with array
test_array=(14 12 23.5 16 19.34)
total=$(sum_array "${test_array[@]}")
echo "The total sum of the test array is $total"
crontab
# Create a schedule for 30 minutes past 2am every day
30 2 * * * bash script1.sh
# Create a schedule for every 15, 30 and 45 minutes past the hour
15,30,45 * * * * bash script2.sh
# Create a schedule for 11.30pm on Sunday evening, every week
30 23 * * 0 bash script3.sh
'Language > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python 가상환경(venv) 만들기 & requirements.txt 관리하기 (0) | 2023.01.29 |
|---|---|
| 데이터 엔지니어(아홉번째 이야기) (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| 데이터 엔지니어(일곱번째 이야기) (0) | 2021.10.14 |
| 데이터 엔지니어(다섯번째 이야기) (0) | 2021.10.07 |
| 데이터 엔지니어(네번째 이야기) (0) | 2021.09.16 |


댓글